SR 11302
CAS No. 160162-42-5
SR 11302( —— )
Catalog No. M27717 CAS No. 160162-42-5
SR 11302 is an inhibitor of activator protein-1 (AP-1).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 115 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 178 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 357 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 557 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 795 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSR 11302
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSR 11302 is an inhibitor of activator protein-1 (AP-1).
-
DescriptionSR 11302 is an inhibitor of activator protein-1 (AP-1).(In Vitro):SR 11302 can inhibit the growth of breast cancer cell line T-47D, the lung cancer line Calu-6, and HeLa cells. SR 11302 had very little effect on either the proliferation or the differentiation of HL-60, fresh APL, and NB4 cells.(In Vivo):In an AP-1-luciferase transgenic mouse carcinogenesis model, SR11302 significantly inhibits both AP-1 activations in 7,12-dimethyl benz(a)anthracene-initiated mouse skin and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced papilloma formation.
-
In VitroSR 11302 (SR11302) show strong anti-AP-1 activity with selective binding with RARα and RARγ, but not with RARβ and RXRα. SR 11302 (SR-11302; 1 μM) inhibits AP-1 transcription factor activity and decreases aldosterone levels by 61.9% in hypoxia-treated cells. SR 11302 (SR-11302; 2 μM; 48 hours) inhibits Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-induced cell proliferation in adenocarcinoma gastric (AGS) cells.SR 11302 (2 μM; 24 hours) inhibits H. pylori-induced expression of β-catenin and c-myc in AGS cells.
-
In VivoSR 11302 (SR11302; low dose 0.5 mg/kg and high dose 1 mg/kg body weight; orally gavaged daily) treatment reduces the total vascular lesion number and lesion size in Vldlr-/- mice in a dose-dependent manner. Animal Model:Vldlr-/- mice Dosage:Low dose 0.5 mg/kg and high dose 1 mg/kg body weight Administration:Orally gavaged daily from P5 to P15 Result:High-dose from P5 to P15 reduced the total vascular lesion number by 48% and decreased the lesion size by 40%, without detectable signs of toxicity in mice, including no change in body weight.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
Recptor11β-HSD1|Gap Junction Protein
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number160162-42-5
-
Formula Weight376.54
-
Molecular FormulaC26H32O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (66.40 mM)
-
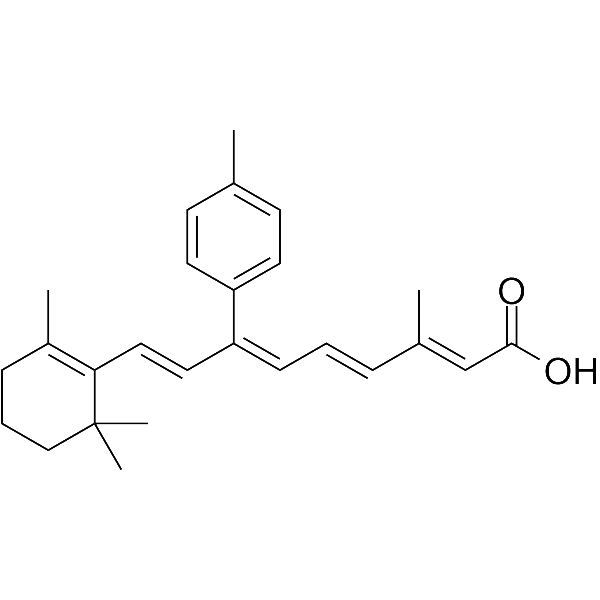
SMILESCC(C=CC=C(C=CC1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)c1ccc(C)cc1)=CC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Azarashvili T, et al. Carbenoxolone induces permeability transition pore opening in rat mitochondria via the translocator protein TSPO and connexin43. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Sep 15;558:87-94.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dacarbazine
Dacarbazine(DTIC-Dome) is an antineoplastic chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of various Ys, among them malignant melanoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, sarcoma, and islet cell carcinoma of the pancreas.
-
Fosifloxuridine nafa...
NUC-3373 (Fosifloxuridine nafalbenamide), a pyrimidine nucleotide analogue, is a Thymidylate synthase inhibitor.NUC-3373 has anticancer activity.
-
Gallium maltolate
Gallium maltolate is a ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


